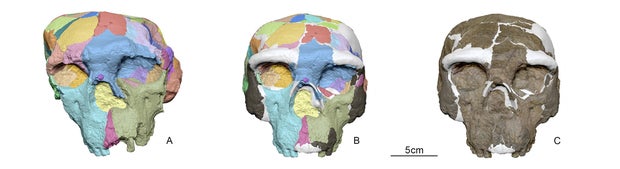
A digital reconstruction of a skull of one million people suggests that humans may have diverged from our old ancestors 400,000 years earlier than thought and in Asia, not in Africa, a study revealed.
The results, published Thursday, are based on the reconstruction of a crushed skull discovered in China in 1990 and have the potential to resolve the “long -standing confusion in the environment” of human evolution, researchers said.
But experts not involved in the work warned that the results were likely to be disputed and underlined the current uncertainties in the chronology of human evolution.
The skull, labeled Yunxian 2, previously belonged to a human precursor called Homo erectus.
But modern reconstruction technologies have revealed that characteristics closer to a species before did not exist until later in human evolution, including recently discovered homo and our own homo sapiens.
“It changes a lot of reflection,” said Chris Strunger, anthropologist at the Natural History Museum, London, who was part of the research team.
“This suggests that in the 1 million years ago, our ancestors had already divided into distinct groups, pointing towards a much more previous and more complex human scission than we thought before,” he added.
The results shocked the research team.
“From the start, when we got the result, we thought it was incredible. How could it be so deep in the past?” Xijun Ni, professor at the University of Fudan who co-directed the analysis, told BBC News. “But we have tested it again and again to test all the models, use all the methods, and we are now confident on the result, and we are in fact very excited.”
Jiannan Bai and Xijun Ni / Handout via Reuters
If the results are correct, this suggests that there may be members much earlier from other early hominins, including Neanderthals and Homo Sapiens, the researchers said.
He “muddies the waters” on long -standing hypotheses that the first humans dispersed from Africa, said Michael Petraglia, director of the Australian research center of the University of Griffith for human evolution, which was not involved in the study.
“There is a great potentially change that occurs here, where East Asia now plays a very key role in the evolution of hominines,” he told the France-Press agency.
“Many questions”
Research, published in the Revue Science, used advanced techniques of computed tomography, light imaging and virtual reconstruction to model a complete Yunxian 2. The team then printed replicas on a 3D printer, according to BBC News.
Scientists partially relied on another similar skull to shape their model, then compared it to more than 100 other specimens.
The resulting model “shows a distinctive combination of lines”, said the researchers, some similar to Homo Erectus, including a projected lower side.
Jiannan Bai and Xijun Ni / Handout via Reuters
But other aspects, including its apparently larger brain capacity, are closer to Homo Longi and Homo Sapiens, according to the study.
“Yunxian 2 can help us solve what is called” confusion in the middle “, the confusing range of human fossils between 1 million to 300,000 years,” Stranger said in a press release.
A large part of human evolution remains debated, and Petraglia said that the results of the study were “provocative” although based on solid work.
“It’s a sound, but I think the jury has always been released. I think there will be a lot of questions raised,” he said.
Andy Herries, archaeologist at the University of Trobe, said that he was not convinced by the conclusions and that genetic analysis had shown a fossil morphology, or form, was “not always a perfect indicator for human evolution”.
“They have this interpretation that I just don’t really think of taking into account the genetic stories of these things we know,” he told AFP.
Dr. Aylwyn SCALLY, an evolutionary geneticist at the University of Cambridge, told BBC News that although the study conclusions were plausible, they were far from being certain and that more evidence had to be sure.
“This image is not yet clear to us, so if the conclusions of this research are supported by other analyzes, ideally from certain genetic data, then I think we would start to be more and more confident on this subject,” he told BBC News.
Xijun Ni / Handout via Reuters
The results are only the latest in a series of recent research that complicated what we thought about our origins.
Homo longi, Also known as “Dragon Man”, “ was himself named only as a new species and a close human parent in 2021, by a team that included Strnger.
The authors said that their work illustrates the complexity of our shared history.
“Fossils like Yunxian 2 show how much we still have to learn about our origins,” said Stringer.